阅读了struts2的部分源码, 才知道, 原来struts2是不用servlet的, 只用了filter就可以实现所有的功能, 包括action和interceptor.
首先, 一个请求过来, filter会拦截到, 通过解析请求URL, 得到请求的target(哪个类的哪个方法), 放在actionMapping里边, 这个通过actionMapping可以得到要执行的类的方法, 然后作为对象放到DefaultActionInvocation这个类中, 这个类是实现了ActionInvocation的类, 没错, 就是在struts2的拦截器方法intercept(ActionInvocation invocation)的参数类型.把代码罗列出来比较容易看.
先看看FilterDispatcher这个filter的doFilter方法
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext();
String timerKey = "FilterDispatcher_doFilter: ";
try {
// FIXME: this should be refactored better to not duplicate work with the action invocation
ValueStack stack = dispatcher.getContainer().getInstance(ValueStackFactory.class).createValueStack();
//这里就是为什么我们可以在action中直接使用ActionContext.getContext().getRequest()
//来得到当前的request等对象了. 用的是ThreadLocal的存储.
ActionContext ctx = new ActionContext(stack.getContext());
ActionContext.setContext(ctx);
UtilTimerStack.push(timerKey);
request = prepareDispatcherAndWrapRequest(request, response);
ActionMapping mapping;
try {
mapping = actionMapper.getMapping(request, dispatcher.getConfigurationManager());
} catch (Exception ex) {
log.error("error getting ActionMapping", ex);
dispatcher.sendError(request, response, servletContext, HttpServletResponse.SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR, ex);
return;
}
if (mapping == null) {
// there is no action in this request, should we look for a static resource?
String resourcePath = RequestUtils.getServletPath(request);
if ("".equals(resourcePath) && null != request.getPathInfo()) {
resourcePath = request.getPathInfo();
}
if (staticResourceLoader.canHandle(resourcePath)) {
staticResourceLoader.findStaticResource(resourcePath, request, response);
} else {
// this is a normal request, let it pass through
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
// The framework did its job here
return;
}
dispatcher.serviceAction(request, response, servletContext, mapping);
} finally {
try {
ActionContextCleanUp.cleanUp(req);
} finally {
UtilTimerStack.pop(timerKey);
}
}
}
很明显, 这是调用了 Dispatcher.serviceAction的方法来调用action的. 继续往下看serviceAction方法
public void serviceAction(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, ServletContext context,
ActionMapping mapping) throws ServletException {
Map<String, Object> extraContext = createContextMap(request, response, mapping, context);
// If there was a previous value stack, then create a new copy and pass it in to be used by the new Action
ValueStack stack = (ValueStack) request.getAttribute(ServletActionContext.STRUTS_VALUESTACK_KEY);
boolean nullStack = stack == null;
if (nullStack) {
ActionContext ctx = ActionContext.getContext();
if (ctx != null) {
stack = ctx.getValueStack();
}
}
if (stack != null) {
extraContext.put(ActionContext.VALUE_STACK, valueStackFactory.createValueStack(stack));
}
String timerKey = "Handling request from Dispatcher";
try {
UtilTimerStack.push(timerKey);
String namespace = mapping.getNamespace();
String name = mapping.getName();
String method = mapping.getMethod();
Configuration config = configurationManager.getConfiguration();
ActionProxy proxy = config.getContainer().getInstance(ActionProxyFactory.class).createActionProxy(
namespace, name, method, extraContext, true, false);
request.setAttribute(ServletActionContext.STRUTS_VALUESTACK_KEY, proxy.getInvocation().getStack());
// if the ActionMapping says to go straight to a result, do it!
if (mapping.getResult() != null) {
Result result = mapping.getResult();
result.execute(proxy.getInvocation());
} else {
proxy.execute();
}
// If there was a previous value stack then set it back onto the request
if (!nullStack) {
request.setAttribute(ServletActionContext.STRUTS_VALUESTACK_KEY, stack);
}
} catch (ConfigurationException e) {
// WW-2874 Only log error if in devMode
if(devMode) {
String reqStr = request.getRequestURI();
if (request.getQueryString() != null) {
reqStr = reqStr + "?" + request.getQueryString();
}
LOG.error("Could not find action or result\n" + reqStr, e);
}
else {
LOG.warn("Could not find action or result", e);
}
sendError(request, response, context, HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND, e);
} catch (Exception e) {
sendError(request, response, context, HttpServletResponse.SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR, e);
} finally {
UtilTimerStack.pop(timerKey);
}
}
通过前面传的参数, 得到一个ActionProxy的代理对象, 不论是执行result.execute方法还是proxy.execute方法, 最红都会调用到 StrutsActionProxy 的 execute()方法, 该方法内容如下:
public String execute() throws Exception {
ActionContext previous = ActionContext.getContext();
ActionContext.setContext(invocation.getInvocationContext());
try {
return invocation.invoke();
} finally {
if (cleanupContext)
ActionContext.setContext(previous);
}
}
看到了吧, 这就是action调用的入口, ActionInvocation.invoke()!!!!默认实现是怎样的呢?看代码:
public String invoke() throws Exception {
String profileKey = "invoke: ";
try {
UtilTimerStack.push(profileKey);
if (executed) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Action has already executed");
}
if (interceptors.hasNext()) {
final InterceptorMapping interceptor = (InterceptorMapping) interceptors.next();
String interceptorMsg = "interceptor: " + interceptor.getName();
UtilTimerStack.push(interceptorMsg);
try {
resultCode = interceptor.getInterceptor().intercept(DefaultActionInvocation.this);
}
finally {
UtilTimerStack.pop(interceptorMsg);
}
} else {
resultCode = invokeActionOnly();
}
// this is needed because the result will be executed, then control will return to the Interceptor, which will
// return above and flow through again
if (!executed) {
if (preResultListeners != null) {
for (Object preResultListener : preResultListeners) {
PreResultListener listener = (PreResultListener) preResultListener;
String _profileKey = "preResultListener: ";
try {
UtilTimerStack.push(_profileKey);
listener.beforeResult(this, resultCode);
}
finally {
UtilTimerStack.pop(_profileKey);
}
}
}
// now execute the result, if we're supposed to
if (proxy.getExecuteResult()) {
executeResult();
}
executed = true;
}
return resultCode;
}
finally {
UtilTimerStack.pop(profileKey);
}
}
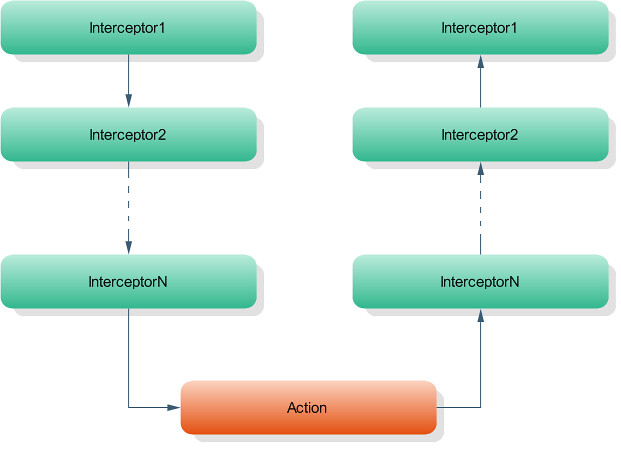
这里的代码简直是荡气回肠, 回想一下, 我们在应用interceptor的时候, 是可以在action执行前作一些操作, 在action执行后也做些操作, 那么 一个配置了多个interceptor的action 如何保证他制备执行一次呢?这里用到了反射的间接递归. DefaultActionInvocation类里边有个intercepters成员, 这个成员是Iterator类型的, 其实就是一个迭代器, 通过迭代他可以按顺序执行interceptors, 而只有在执行了最后一个interceptor之后, 才会执行action的方法, 这样能保证action制备执行一次, 而且执行的前后都能被拦截, 精髓啊, 这段代码.
if (interceptors.hasNext()) {
final InterceptorMapping interceptor = (InterceptorMapping) interceptors.next();
String interceptorMsg = "interceptor: " + interceptor.getName();
UtilTimerStack.push(interceptorMsg);
try {
resultCode = interceptor.getInterceptor().intercept(DefaultActionInvocation.this);
}
finally {
UtilTimerStack.pop(interceptorMsg);
}
} else {
resultCode = invokeActionOnly();
}
}
从这段代码我们也可以看出, 如果action的interceptors能全部执行完, 那么最先执行的interceptor将最后结束.如下:
以上, struts2只是从filter 得到actionMapping, 然后交给dispacher处理, 无需servlet, 我觉得是为了让编程人员可以从request中得到正确的url和refferer等信息吧, 如果通过filter, 然后交给servlet去处理, 那么request中的东西会发生变化.
发表评论
沙发空缺中,还不快抢~